The description tag (called meta descriptino here) is one of two components (along with the title tag) that make up the user’s gateway to a specific web page from the search results page. Here’s everything you need to know.
Ever tried to think about how Google users make decisions?
How do users know whether a particular search result displayed to them on the search results page is relevant to them?
Well, that’s not a simple question. The probable surfer uses a wide range of criteria to understand whether he should click on the first result on the search results page, or maybe the second or, even, the third.
When a reviewer searches the search results page, he searches for various features to indicate that the result presented to him is relevant to his intention and the phrase he was looking for.
It is very important to understand: every user is a complete world, and the search engine cannot guess which situation the user is in when he searches.
That is, the search engine does not know whether the user, while searching, is stressed, disturbed, angry, happy, whether he is seeking in-depth and long-term knowledge, or a simple and laconic answer.
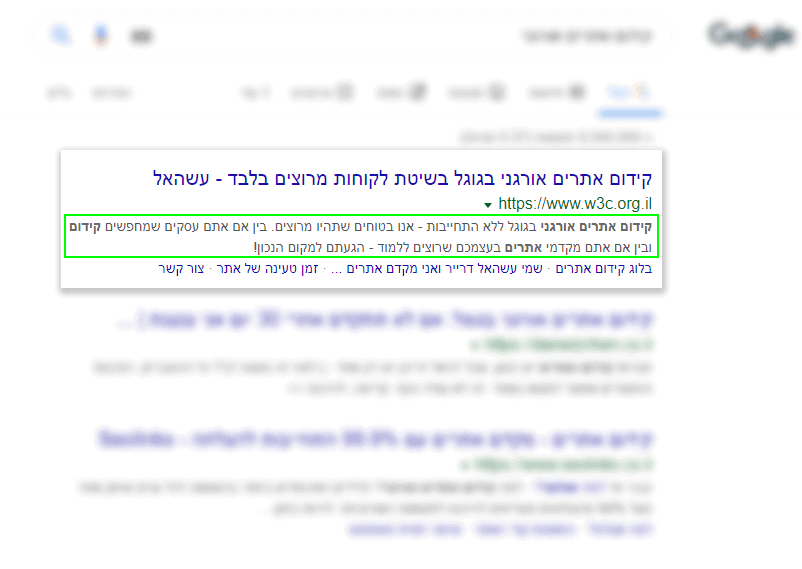
How does a description tag/ meta description help the user decide whether the search result is relevant to him?
The description tag appears on the search results page immediately after the title tag, for each page to which the users are directed. A description tag that is formatted for the surfer can help him identify with the writing, and decide that this is a suitable page for him.
Because some of the considerations that guide a user to click or not to click a link on the search results page are the mood they are in, and current events that occurred near to a search that they performed. Also, possible that a well-formatted meta description will work one day while another day, for the same user, will work less well.
A good description tag will usually contain an eye-catching, over-the-top paragraph, which will include the main keywords or synonyms.
In some cases, the words searched by the user, or their various biases, will be highlighted in the description field displayed on the search results page for each page.
This is one indication of many kinds, which aims to signal to the surfer that the result shown is relevant to him, and why. A good description tag will be neither too long nor too short, and will fit all possible views: on your computer, tablet or mobile device.
Trial and error in successful meta discrepancy creation
Trial and error are integral to the process of updating meta discrepancies on the site.
There is no magic formula. No code word. There are times when using powerful and exciting words can help increase your CTR and there are other times when actually displaying your keywords in a cold way and without style will do the job.
Precisely for this purpose, site promoters perform constant time and error to evaluate the effectiveness of usage of meta discrepancies in site pages.
Does Google make a commitment to using the meta-description we set for a particular page?
The answer is, of course, negative.
Google uses the meta-description that we have set up on a site if it thinks it is the most successful description that can be put on a site, of the content elements that already exist on the page.
In many cases, Google uses the H1 and H2 headlines to create a more successful meta-description for its search engines.
Does Google use meta descriptive as a factor in page rank on the site?
The common assumption in the SEO world is that a description tag is not used directly as a factor in the site’s ranking.
However, a good formulation of the meta-description field for a site’s page can help increase user click-through rates (CTRs), which in itself can transmit to Google that this is a relevant result for many users.
The CTR is, in fact, the ratio of the number of users who choose to click on a particular search result, and the number of users in that result was presented to them on the search results page.
In conclusion
The meta description tag, along with the title tag, is the front door for searchers to search from your site. Proper formulation of meta-discrepancy will help your surfers make a decision and click the link to the site.
The meta-discrepancy shown on the search results page is not in your exclusively control, the site owners and Google may decide that it provides the user with another relevant description that it is able to compile from the various content on the page. Trial and error will be useful to get the most successful CTR result by updating the description tag field.